Glossary of Terms
- Terms Used in Writing Skills
- Terms Used in Arranging 1
- Terms Used in Arranging 2
- Terms Used in Chord Scale Voicings
- Terms Used in Ear Training
- Terms Used in Harmony 1
- Terms Used in Harmony 2
- Terms Used in Harmony 3
- Terms Used in Harmony 4
- Terms Used in Introduction to Music Technology
Terms Used in Writing Skills
• beam: In music notation, the horizontal or near-horizontal line (or lines) that connects the stems of two or more notes, each less than a quarter note in value, occuring consecutively within a beat. In some cases, primarily with eighth notes, beams may encompass more than one beat and up to two beats. There are two basic types of beams: primary beams and secondary beams.
• Primary beams link entire note groups together.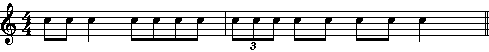
•Secondary beams define further subdivisions of a note-group beamed together by a primary beam.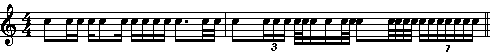
• Binary Form - Music which is divided into two parts.
• Imaginary (invisible) Barline - Showing the beginning of a beat through the beaming of groups of eighth notes, sixteenth notes, or triplets in certain time signatures, the most common of which are 4/4, 6/8, 12/8, cut-time. In 4/4 and cut-time, the grouping of eighth notes should show the start of beat three and the grouping of 16th notes and triplets must show the start of all four beats. In 6/8, the fourth eighth note must be visible. In 12/8, the seventh eighth note must be visible. Beams on eighth notes, sixteenth notes, or triplets should not cross over the imaginary barline.
Terms Used in Arranging 1
Also see Terms Used in Writing Skills
• Anticipation - A technique of melodic or rhythmic alteration which changes a note that occurs on-the-beat to be played early resulting in syncopation. The most common anticipations occur one-half beat early (an 8th note anticipation), a quarter-of-a-beat early (a 16th note anticipation), or one-third of a beat early (a triplet anticipation). When the anticipation occurs in the melody, it is a melodic anticipation. Anticipations are sometimes also called "pushed notes" or "pushes."
• Chord Tone - the pitches in a chord that determine its basic sound quality. Chord tones are the following:
a. root, 3rd and 5th of a triad (major, minor, augmented or diminished).
b. root, 4th and 5th of a triad (sus 4 triad).
c. root, 3rd, 5th and 7th of seventh chords.
d. root, 4th, 5th and flat 7th of a dominant 7th sus 4 chord.
e. root, 3rd, 5th and 6th of a sixth chord (major, minor).
• Delayed Attack - A technique of melodic or rhythmic alteration which changes a note that occurs on-the-beat to be played one-half beat late (an 8th note delayed attack or hesitation), a quarter-of-a-beat late (a 16th note delayed attack), one-third of a beat late (a triplet delayed attack), or one full beat late. The opposite of an anticipation. Delayed attacks are also commonly called "hesitations." As with anticipations, the result is syncopation.
• Tension - a note (or notes) added to a major triad, minor triad, or sixth chord which represent the logical upper extensions of the triad (using intervals of a 3rd). The following notes in a chord are considered tensions: 7, b7, 9, b9, #9, 11, #11, 13, b13.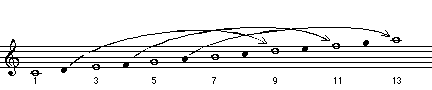
These upper extension notes create "tense" musical and intervallic relationships with the pitches of the major or minor triad in the chord. The chords that contain tension notes sound somewhat more unstable than a 7th chord does. This is because the tensions "rub" against the other notes in the chord. Tensions create intervals of a richer or denser quality within the chord structure than those resulting from only the basic chord functions (root, 3rd and 5th). The 7th of a chord is often considered a chord tone, rather than a tension.
Tensions are considered non-chord tones (also called nonharmonic tones), rather than chord tones, even when they are part of a chord. Tensions enhance or enrich the sound of the chord, and modifies the basic quality of the chord sound. While a major chord with tensions still has a major quality as part of its sound, tension notes can mask the quality of the overall sound. Adding a sharp nine tension to a dominant 7th chord is an example of such a mixture.
See also Available Tensions in Terms Used in Harmony 1
Terms Used in Arranging 2
Also see Terms Used in Writing Skills and Terms Used in Arranging 1
• Guide Tone Line - a unison background line which leads stepwise or through common tones of the harmonic progression, providing an effective counterline accompaniment to the melody.
• Low Interval Limit - The lowest point of an interval (from minor second to major 10th) below which the interval begins to sound muddy or indistinct. The limits are not absolutes, but represent areas below which there is a real risk that the resultant sound will not work well within a normal harmonic context.
• Spread Voicing - Open voicings of chords with the root of the chord on the bottom; sometimes referred to as "pads".
Terms Used in Chord Scale Voicings
Also see Terms Used in Writing Skills, Terms Used in Arranging 1, and Terms Used in Arranging 2
• Chord Scale - A specific set of scalewise pitches that include the chord tones and available tensions of a given chord, along with any passing tones that help definre the tonal or modal context of the chord.
• Modal Interchange - Using chord structures and their chord scales from a parallel (having the same pitch axis) mode or scale.
•Ear Training: Music training that improves the skill of music translation. That skill is utilized in almost all aspects of music: music recognition, music reading, performing and composing. The training consists of rhythmic, melodic (Solfege), and harmonic (chords and progressions) study, as well as performance and dictation.
• Solfege: A system of melodic organization that uses syllables (DO RE MI FA SOL LA TI DO) to designate pitches. Two common systems are Moveable-DO Solfege and Fixed-DO Solfege.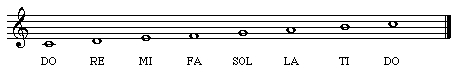
• Moveable-Do Solfege: A method of solfege in which the root or tonic of the key is always "DO." This method focuses on understanding the melodic functions common to each key. This is the method used in the Berklee Ear Training courses.
• Fixed-DO Solfege: A method of solfege in which the note "C" is always DO, regardless of the key. This system focuses on intervallic hearing.
• Dictation: The process of translating music that is heard. Dictation is done either by performing (sing-back or play-back), and/or by notating the music.
Terms Used in Harmony 1
• Modes: Refers to the scales that are displacements of the major scale.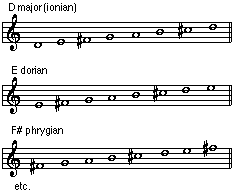
• Triad: A chord containing three notes, usually consisting of a root, a third above the root and a fifth above the root.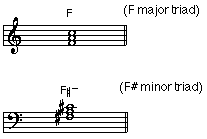
• Seventh Chord: A chord containing four notes, usually consisting of a triad with a seventh above the root.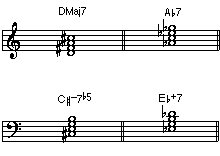
• Available Tensions: Tensions are notes added to a seventh chord by extending the chord upwards in thirds. Tensions are measured intervallically above the root of the chord, and can consist of a minor, major or augmented ninth, a perfect or augmented eleventh and/or a minor or major thirteenth. Not every tension will work with every chord type. The ones that do work with a specific chord type are said to be "available".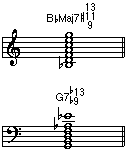
See also Tension in Terms Used in Arranging 1
• Diatonic Progression: Harmony made up exclusively of notes from the scale of the key.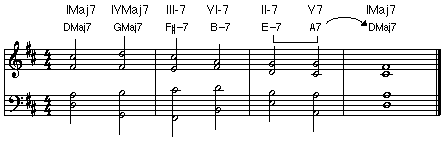
Terms Used in Harmony 2
Also see Terms Used in Harmony 1
• Secondary Dominants: Dominant chords that are expected to resolve down a perfect fifth to a diatonic chord other than I. For example: V7/II (V7 of II), V7/III (V7 of III)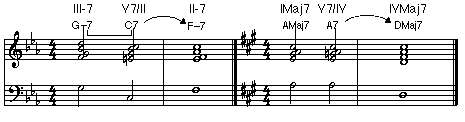
• Extended Dominants: A series of dominants without a direct key relationship, each one resolving down a fifth to the next.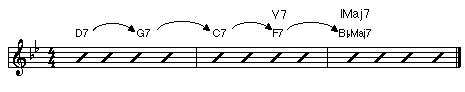
•Modal Interchange: Borrowing chords from a parallel mode. In Harmony 2, borrowing chords from natural minor to use in the parallel major.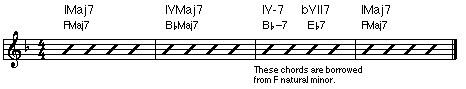
• Harmonic Continuity: Moving the notes of one chord as smoothly as possible to the notes of the next chord (root motion is independent).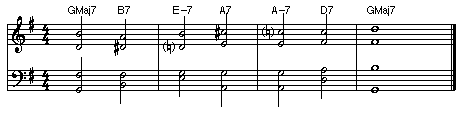
Terms Used in Harmony 3
Also see Terms Used in Harmony 1 and Terms Used in Harmony 2
• Substitute Dominants: Also known as tritone substitutes, dominant seventh chords that contain the same tritone as the dominant chord for which they are substituting. (ex. G7 and Db7, Eb7 and A7, B7 and F7, etc.) Their expected resolution is down a minor second.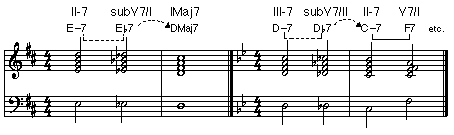
•Diminished Chord: Diminished triad: a chord consisting of a root, minor third and diminished fifth. Diminished seventh chord: a chord consisting of a root, minor third, diminished fifth and diminished seventh.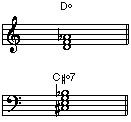
• Modulation: Within a piece of music, a change of tonal center (key) as perceived by the listener.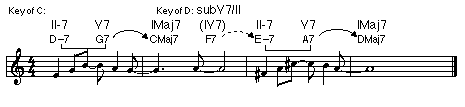
Terms Used in Harmony 4
Also see Terms Used in Harmony 1, Terms Used in Harmony 2, and Terms Used in Harmony 3
• Compound Chord: A chord whose chord symbol consists of more than one element. Also known as a slash chord. For example: G/B (inversion) , Fmaj7/G (hybrid), D (polychord), C7
• Hybrid: A compound chord consisting of upper chord tones (except the third) and tensions above the indicated root. Also known as incomplete chords or chords without thirds.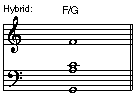
• Inversion: A chord that is voiced with a chord tone other than the root in the bass.
For example: F/A, Gmaj7/D, Eb7/G
•Polychord: A compound chord consisting of an upper chord over a lower chord.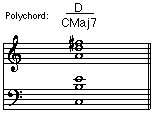
• Constant Structure Progression: A chord progression consisting of three or more chords of the same quality.
Terms Used in Introduction to Music Technology
Students who wish to test out of MTEC-111: Introduction to Music Technology should know the meaning of the following terms and understand their application to music technology in cases where everyday usage is common:
| 1/4" tape A/D ADB ADC Additive synthesis ADSR AES/EBU Aftertouch Aliasing ALU AM Amplitude Analog Analog/Digital Hybrid Aperiodic Apple printer ports Applications ASCII Attenuation Attenuator Auxiliary input Average level Balanced and Unbalanced Connections Band Pass Filter Bandwidth Baud Rate Bi-amplification Binary Bit Bit depth Bits and Bytes Bits of resolution BPM Buffers Buss Byte Cardioid CD-ROM CD-ROM drives Cents Channel Chorus Circuit Clangorous Clipping Clock Close box CMOS Coincident pair Compression Compression/rarefaction Compressor Condenser Microphone Controller Controller Number CPU Crossover CRT D/A, DAC Daisy Chain DASH Databases dB Decay Decibel Decimal Desktop Diaphragm Digital Digitizing pad Disk Disk Drive Disk storage Distortion Documents DOS Doubling DVD Dynamic Microphone Dynamic Range Early Reflection Envelope EPROM Eq Equalizers Expansion Fader Far field File Filters Finder First Reflection Flags Flanging Floppies Floppy Disk FM Synthesis Folder Formant Format Frequency Frequency Response Fundamental Gain Gain-staging Gate Giga Graphic EQ Graphic Equalizer Half Step Hard Disk Hard disks Harmonic Harmonic Spectrum Headroom Hertz Hexadecimal High-pass Filter Hz Impedence Inches Per Second Input Insert Internet IPS Joystick Keyboard Controller Kilo LAN Layering LED Level to tape LFO Librarian Limiter Limiting Loudness Low-pass Filter MacOS Macros Magnetic Flux Magneto-optical Male/female Master Faders MDM Mega Memory Menu MIDI MIDI controllers MIDI Interface Millivolt Mini plug Mixing board (console, desk) Mode Modem Monitor Loudspeaker Monitor/cue mix Mono Mouse Moving Multi-effects Multi-sampling Multi-tasking Multi-timbral Mute |
Near field Networks Noise Reduction Non-harmonic Non-normalled Normalled Nyquist Nyquist Frequency Octave Omni-directional Operating systems Optical Oscillator Output Overtones Oxide Pan Parallel Parallel communications Parallel interface Parametric EQ Partial PC printer ports Peak level Periodic Peripherals, Permanent magnet Phantom power Pickup Patterns Pitch Pitch Bend Pitch Shifting Plotter Polar Pattern Polyphonic Polyphony Port Post-fader Power Bandwidth Pre-delay Pre-Fader Pre-fader Preamp Preamplifiers Precedence effect Preset Printer Printhrough Program Program change Protocols Proximity effect Pull-Down Menus PZM Q Quantization RAM Ratio RCA jack Real-time Release Removable hard disks Resolution Resonance Return Reverb Reverberation and Delay Ribbon Microphone ROM Rotating head S/PDIF Sample playback Sample Rate Sample rate Samplers Save SCSI Send Sequencer Sequencing Serial Serial communications Serial Interface Shelving EQ Signal Processing Signal-to-Noise Ratio Sine Sizing Slapback Snake Solo Song position pointer Sound design Sound engine Sound Module Sound System Soundfile Spaced pair Spectrum SPL Splitter Transformer Spreadsheets Stack Stage Box Star network?Ring network?Nodes Step input Stereo Storage Subtractive Synthesis Summing Sustain Pedal Synchronization Synthesizer Synthesizer Voice System Exclusive System Folder System real-time Tape Hiss Tape storage Tape Width Threshold Timbre Touch screens Touch sensitive Track Track Width Transducer Transient response Transients Trash can Tri-amplification Trim TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) Tweeter Unbalanced Unix VCA/DCA VCO/DCO Velocity Voice Voice coil Volt Von Neumann architecture VU Waveform Wavetable Synthesis Web Wheel Windows Windows 3.1, 95, and 98 Woofer Word processing Wow & Flutter XLR |
